Treatments
- Treatments
- Diagnostic Angiograms & Venograms
- Angioplasty & Stent Placement
- Aortic & Peripheral Stent-Grafts
- Transcatheter Embolization
- Transjugular Liver Biopsy
- TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Porto-Systemic Stent Shunt)
- Intra-arterial & Venous Thrombolysis
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter Placement
- Biliary Drainage Procedures
- Nephrostomy Tube & Nephroureteral Stent Placement
- Fallopian Tube Recanalization
- Musculoskeletal Embolization (Knee OA, Plantar Fasciitis)
- Prostatic Artery Embolisation
Angioplasty & Stent Placement
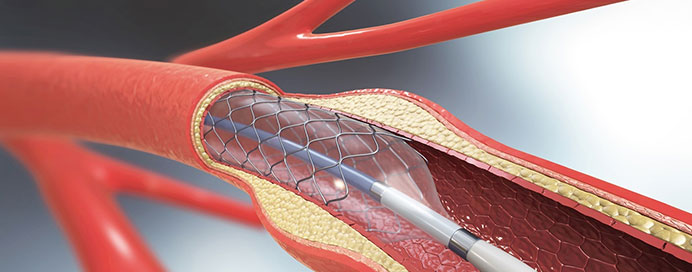
What is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to open narrowed or blocked arteries. A thin catheter with a small balloon at its tip is guided into the affected artery. The balloon is then inflated to widen the artery and restore normal blood flow.
What is Stent Placement?
Often, a stent (a small metal mesh tube) is placed in the artery after angioplasty. The stent helps keep the artery open, preventing it from narrowing again. Some stents are coated with medication to further reduce the risk of blockage.
Procedure
- A catheter is inserted into a blood vessel (usually in the wrist or groin).
- Contrast dye is injected to guide the placement.
- A balloon is inflated to open the artery.
- A stent is placed to support the artery walls.
- The catheter is removed, and the site is bandaged.
Benefits
- Restores blood flow quickly.
- Minimally invasive with faster recovery compared to surgery.
- Reduces symptoms like chest pain, fatigue, or leg pain.
- Lowers the risk of heart attack and stroke.
Risks
- Bleeding or bruising at the insertion site.
- Blood clots forming in the stent.
- Restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery).
- Rare allergic reaction to contrast dye.
