Treatments
- Treatments
- Diagnostic Angiograms & Venograms
- Angioplasty & Stent Placement
- Aortic & Peripheral Stent-Grafts
- Transcatheter Embolization
- Transjugular Liver Biopsy
- TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Porto-Systemic Stent Shunt)
- Intra-arterial & Venous Thrombolysis
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter Placement
- Biliary Drainage Procedures
- Nephrostomy Tube & Nephroureteral Stent Placement
- Fallopian Tube Recanalization
- Musculoskeletal Embolization (Knee OA, Plantar Fasciitis)
- Prostatic Artery Embolisation
Bronchial Artery Embolization
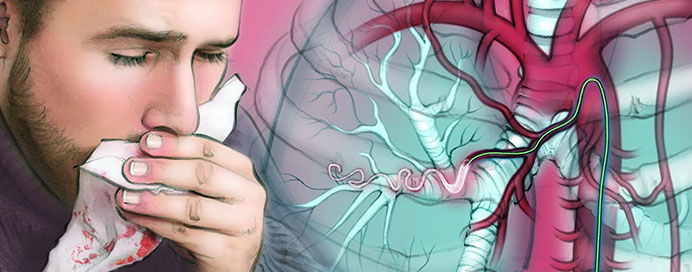
Bronchial Artery Embolization (BAE) is a minimally invasive procedure used to control and treat severe or recurrent bleeding from the lungs (hemoptysis). During the procedure, a catheter is guided into the bronchial arteries, and small particles or coils are injected to block the abnormal blood vessels causing the bleeding. BAE is highly effective, safe, and often avoids the need for surgery in life-threatening cases of hemoptysis.
What it Treats
- Life-threatening or recurrent hemoptysis (coughing up blood)
- Abnormal blood vessels in the lungs due to infections (e.g., tuberculosis), bronchiectasis, lung cancer, or other lung diseases
How it Works
- A catheter is inserted through the groin or arm.
- Imaging is used to locate the abnormal bronchial artery.
- Embolic material (tiny particles or coils) is injected to block the bleeding vessels.
Benefits
- Minimally invasive alternative to surgery
- Quick relief from bleeding
- Shorter recovery time
- Can be repeated if necessary
Risks
- Mild chest pain or discomfort
- Temporary difficulty in swallowing
- Rare risk of non-target embolization (blockage of normal vessels)
