Treatments
- Treatments
- Diagnostic Angiograms & Venograms
- Angioplasty & Stent Placement
- Aortic & Peripheral Stent-Grafts
- Transcatheter Embolization
- Transjugular Liver Biopsy
- TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Porto-Systemic Stent Shunt)
- Intra-arterial & Venous Thrombolysis
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter Placement
- Biliary Drainage Procedures
- Nephrostomy Tube & Nephroureteral Stent Placement
- Fallopian Tube Recanalization
- Musculoskeletal Embolization (Knee OA, Plantar Fasciitis)
- Prostatic Artery Embolisation
Intra-arterial & Venous Thrombolysis
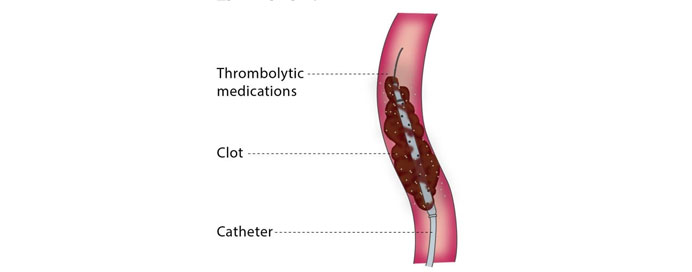
Intra-arterial and venous thrombolysis is a minimally invasive procedure aimed at dissolving blood clots (thrombi) that obstruct arteries or veins. The procedure involves the direct delivery of thrombolytic drugs, such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), into the clot using a catheter guided under fluoroscopy. In arterial thrombolysis, the focus is on treating blockages in arteries, such as in acute limb ischemia, stroke, or coronary artery thrombosis, while venous thrombolysis targets deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or other venous obstructions. The treatment can rapidly restore blood flow, relieve symptoms, and reduce the risk of tissue damage. It is often combined with mechanical thrombectomy in cases of large clots for enhanced efficacy. Careful patient selection is critical due to the risk of bleeding complications.
Indications
- Acute arterial occlusions (e.g., limb ischemia, stroke)
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Pulmonary embolism in select cases
Procedure Steps
- Vascular access via artery or vein (usually femoral)
- Catheter advanced to thrombus under imaging guidance
- Direct infusion of thrombolytic agent into clot
- Optional mechanical clot disruption if needed
Risks
- Bleeding at access site or internally
- Hemorrhagic stroke (rare in arterial thrombolysis)
- Allergic reactions to thrombolytic agents
- Distal embolization
