Treatments
- Treatments
- Diagnostic Angiograms & Venograms
- Angioplasty & Stent Placement
- Aortic & Peripheral Stent-Grafts
- Transcatheter Embolization
- Transjugular Liver Biopsy
- TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Porto-Systemic Stent Shunt)
- Intra-arterial & Venous Thrombolysis
- Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter Placement
- Biliary Drainage Procedures
- Nephrostomy Tube & Nephroureteral Stent Placement
- Fallopian Tube Recanalization
- Musculoskeletal Embolization (Knee OA, Plantar Fasciitis)
- Prostatic Artery Embolisation
Diagnostic Angiograms & Venograms
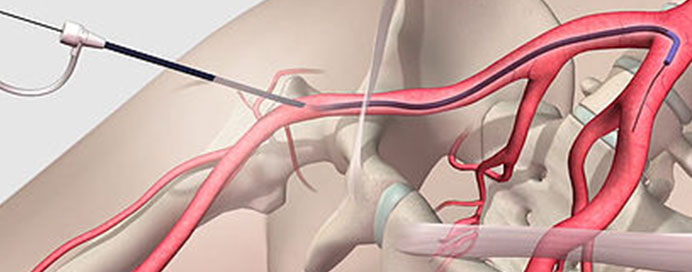
What is an Angiogram?
A diagnostic angiogram is a medical imaging test used to visualize blood vessels (arteries) in detail. A special dye (contrast) is injected into the bloodstream, and X-ray imaging is used to detect blockages, narrowing, or other abnormalities. It is commonly used to evaluate conditions affecting the heart, brain, kidneys, and limbs.
What is a Venogram?
A diagnostic venogram is a similar procedure, but it focuses on the veins instead of arteries. It helps detect problems such as blood clots, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), varicose veins, or venous malformations.
Procedure
- A small catheter is inserted into a blood vessel (commonly in the groin or arm).
- Contrast dye is injected to make blood vessels visible on X-ray images.
- The images are taken in real-time to study the flow of blood.
- The procedure usually takes 30–60 minutes.
Benefits
- Provides a clear and detailed view of blood vessels.
- Helps in early detection of serious vascular conditions.
- Guides doctors to choose the best treatment approach (surgery, stent, medication, etc.).
Risks
- Mild bruising or discomfort at the injection site.
- Allergic reaction to contrast dye.
- Rare chance of infection or bleeding.
- Temporary kidney effects (especially in patients with kidney problems).
Aftercare
- Patients are observed for a few hours.
- Rest is recommended for the day of the procedure.
- Normal activities can usually be resumed the next day.
